Interdepartmental collaboration refers to the process by which individuals from different departments within the same organization work together towards a common goal, sharing knowledge, resources, and expertise. This collaborative approach breaks down traditional silos, fostering a more integrated and holistic approach to achieving organizational objectives. Without it, departments risk operating in isolation, leading to duplicated efforts, conflicting priorities, and missed opportunities.
Effective interdepartmental collaboration is critical to the success of organizations for several reasons. It drives innovation by bringing together diverse perspectives and skillsets, leading to more creative solutions. It improves efficiency by streamlining processes, reducing redundancies, and optimizing resource allocation. Furthermore, it enhances communication and understanding across the organization, fostering a more unified and cohesive work environment. Ultimately, effective collaboration translates to improved productivity, increased profitability, and a stronger competitive edge in the marketplace.
This article will delve into the numerous benefits of interdepartmental collaboration, exploring how it can drive innovation, improve efficiency, and enhance overall organizational performance. We will also address the common challenges that organizations face in fostering effective interdepartmental interaction, offering practical solutions and strategies to overcome these hurdles.
Finally, we will provide useful tips and real-world examples of successful interdepartmental collaboration initiatives, offering a roadmap for organizations looking to cultivate a more collaborative and successful work environment.
Understanding the Concept of Departmental Collaboration
Before diving into strategies and best practices, it’s essential to understand what inter-departmental collaboration truly means and what components make it successful. This section will explore the core concept, distinguish it from similar terms, and break down its fundamental elements that enable organizations to work together effectively.
What is interdepartmental collaboration?
Interdepartmental collaboration, at its core, involves individuals from different departments within the same organization working together towards a shared objective. It’s a structured approach that goes beyond simply communicating between departments. It requires active participation, shared responsibility, and a commitment to achieving a common goal. This differs from cross-departmental collaboration, which often involves a more transactional exchange of information or resources, rather than a deeply integrated working relationship. For a more detailed exploration of cross-departmental collaboration, please refer to our previous article: Your Guide to Effective Cross-Departmental Collaboration
Several key elements contribute to effective interdepartmental collaboration:
- Joint planning and coordination: Successful collaboration begins with a shared understanding of the goals, objectives, and desired outcomes. This requires joint planning sessions where representatives from each participating department contribute their expertise and perspectives. A coordinated plan should clearly define roles, responsibilities, timelines, and communication protocols. This collaborative planning process ensures everyone is on the same page from the outset, minimizing potential conflicts and misunderstandings down the line.
- Sharing resources and information: Open and transparent communication is paramount. Departments must be willing to share relevant information, data, and resources to support the collaborative effort. This includes not only tangible resources like equipment and budget, but also intangible resources like knowledge, expertise, and best practices. Establishing clear channels for communication and information sharing, such as shared platforms or regular meetings, is essential for maintaining transparency and facilitating efficient workflow.
- Setting common goals: Perhaps the most crucial element is the establishment of shared goals. These goals should be clearly defined, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). When departments are working towards a common objective, it fosters a sense of shared purpose and encourages mutual accountability. This alignment of goals ensures that individual departmental efforts contribute to the overall success of the collaborative initiative and the organization as a whole.
By mastering these key elements, organizations can build a strong foundation for effective interdepartmental collaboration that drives innovation, efficiency, and overall organizational success.
👉Interdepartmental vs cross-departmental: What’s the difference? While these terms are often used interchangeably, they have subtle differences. Interdepartmental typically refers to ongoing, structured collaboration between established departments within an organization, focusing on long-term relationships and permanent processes. Cross-departmental often describes more temporary or project-specific collaboration that may involve multiple departments working together for a limited time or specific goal.
Explore Our Use Cases for Team Management
Importance and Benefits of Interdepartmental Collaboration
In this section, we’ll explore why interdepartmental collaboration is crucial for modern businesses and examine the significant benefits it brings to organizations. From operational improvements to employee development, we’ll see how breaking down departmental barriers can transform organizational performance and culture.
Why is interdepartmental collaboration important?
Let’s explore the key reasons why inter-departmental collaboration has become indispensable for modern businesses.
Improved operational efficiency
When departments collaborate effectively, they bring diverse perspectives to decision-making processes, leading to more informed and comprehensive solutions. For example, when a product development team works closely with customer service, they can incorporate real customer feedback into new features, resulting in products that better meet market needs. Similarly, when finance and operations departments collaborate on budgeting, they can create more realistic and achievable financial plans based on operational realities.
Increased innovation
Cross-pollination of ideas between departments often sparks innovation that wouldn’t be possible within siloed teams. Consider how Pixar’s success stems from their practice of having animators, storytellers, and technical experts collaborate closely throughout the creative process. This interdepartmental approach has consistently led to groundbreaking advances in both storytelling and animation technology.
Reduced silos and improved corporate culture
When departments work together regularly, organizational silos naturally break down, fostering a more unified company culture. For instance, when marketing and sales departments align their efforts, they not only achieve better results but also develop a shared understanding and appreciation of each other’s challenges and contributions.
Main benefits of interdepartmental collaboration
While the importance of interdepartmental collaboration is clear, understanding its specific benefits helps organizations recognize the tangible value it brings. These benefits extend beyond immediate operational improvements to create lasting positive impacts across the entire organization. Let’s examine these key advantages:
Optimization of business processes
Interdepartmental collaboration eliminates redundant efforts and streamlines workflows. When departments communicate effectively, they can identify overlapping tasks and create more efficient processes. For example, implementing a shared project management system across departments can reduce duplicate data entry, save time, and ensure everyone works from the same information.
More effective problem solving
When departments pool their knowledge and experiences, they can tackle challenges more effectively. A technical issue that seems insurmountable to one department might have a simple solution when viewed through another department’s expertise. This collaborative approach ensures more robust and creative problem-solving.
Improved communication and removal of barriers
Regular collaboration naturally breaks down communication barriers and builds understanding between departments. As teams work together more frequently, they develop shared vocabularies and better appreciation for each other’s roles. This improved understanding leads to smoother interactions and fewer misunderstandings.
Increased employee engagement
When employees collaborate across departmental lines, they gain a clearer picture of how their work contributes to the organization’s larger goals. This understanding often leads to higher job satisfaction and stronger commitment to the company’s mission. Employees feel more connected to the bigger picture and take pride in their collective achievements.
Creation of a positive work environment
Collaborative environments foster better decision-making and create a more supportive workplace culture. When employees feel their input is valued and they have support from multiple departments, they’re more likely to take positive risks and propose innovative solutions. This supportive atmosphere can significantly improve workplace morale and productivity.
Enhanced professional growth
Interdepartmental collaboration provides valuable learning opportunities for employees. Working with colleagues from different departments exposes them to new perspectives, skills, and ways of thinking. For instance, a marketing professional collaborating with the IT department might gain valuable technical insights, while IT staff can develop better communication skills through the partnership. These cross-functional experiences enhance career development and create more well-rounded professionals.
Through these various benefits, interdepartmental collaboration creates a powerful multiplier effect, where improvements in one area often lead to positive changes in others, creating a virtuous cycle of organizational improvement and success.
👉 Interdepartmental сollaboration vs interdepartmental communication: What’s the difference? Interdepartmental communication is one component of interdepartmental collaboration—it’s the exchange of information between departments. Collaboration is broader, encompassing not just communication but also joint planning, shared resources, common goals, and collective action. Think of communication as the foundation that enables collaboration to occur.
Common Problems of Interdepartmental Collaboration
This section will explore the common challenges that organizations face when striving for effective inter-departmental collaboration. Understanding these potential roadblocks is the first step towards implementing strategies to overcome them and foster a more collaborative and productive work environment.
Common difficulties in interdepartmental collaboration
Several factors can hinder effective inter departmental collaboration:
- Lack of trust and open communication: A lack of trust between departments can lead to reluctance to share information, withholding of resources, and an unwillingness to work together openly. Communication barriers, exacerbated by differing departmental jargon or communication styles, can further complicate matters.
- Conflicting priorities and inconsistent goals: Departments often have their own specific priorities and objectives, which can conflict with those of other departments. This misalignment of goals can create tension and competition, making it difficult to work towards a shared purpose.
- Structural barriers: Traditional organizational structures that silo departments can limit interaction and communication between interdepartmental teams. When employees are confined to their own departmental bubbles, they have fewer opportunities to build relationships and understand the perspectives of colleagues in other areas.
- Hierarchical barriers between leadership and employees: A lack of open communication and feedback between leadership and employees can stifle collaboration. When employees feel their voices are not heard or their contributions are not valued, they are less likely to actively participate in inter-departmental initiatives.
- Lack of resources and time for coordination: Effective collaboration requires dedicated time and resources for planning, communication, and execution. When departments are already stretched thin, it can be difficult to prioritize collaborative efforts, leading to rushed planning and inadequate execution.
- Employee resistance to change: Introducing new collaborative processes often requires changes to established workflows and routines. Resistance to change among employees can hinder the adoption and successful implementation of collaborative initiatives.
- Lack of accountability: When responsibilities are not clearly defined and there is no clear ownership of outcomes, it can lead to diffusion of responsibility and a lack of accountability. This can result in missed deadlines, unmet objectives, and decreased overall effectiveness.
- Difficulty using technology: While technology can facilitate collaboration, it can also present challenges. Employees may struggle to adapt to new tools or platforms, hindering communication and information sharing.
👉 What is interdepartmental coordination? Interdepartmental coordination is the process of organizing and synchronizing activities between different departments to achieve organizational goals efficiently. It involves aligning schedules, resources, and efforts to ensure smooth workflows and avoid duplications or conflicts. This coordination can be formal (through established processes) or informal (through regular communication and relationships).
How to avoid problems
Fortunately, many of these challenges can be proactively addressed through careful planning and implementation of the following strategies:
- Create an environment of trust and transparency: Foster open communication and encourage information sharing. Highlight the interdependence of departmental tasks and demonstrate how collaboration benefits everyone involved. Celebrate shared successes to build trust and reinforce the value of working together.
- Set clear and distinct goals and KPIs: Establish clear, measurable goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) for both individual departments and the collaborative effort as a whole. This ensures everyone understands what they are working towards and how their contributions will be measured.
- Encourage open communication between departments: Implement communication channels and platforms that facilitate easy and transparent communication between departments. Regular inter departmental meetings, shared workspaces, and collaborative software can help break down communication silos.
- Use centralized tools for planning and communication: Utilize project management software, shared calendars, and other centralized tools to streamline communication, track progress, and manage tasks effectively. This ensures everyone has access to the same information and can stay aligned on project timelines and deliverables.
- Conduct regular surveys and collect feedback: Regularly solicit feedback from employees across all departments to identify potential roadblocks, address concerns, and continuously improve the collaborative process. This demonstrates a commitment to employee input and helps create a more inclusive and effective collaborative environment.
👉 What is an example of interdepartmental collaboration? A classic example is a product launch where multiple departments work together: Product Development creates the product, Marketing develops promotional materials, Sales prepares the go-to-market strategy, Legal ensures compliance, Finance handles pricing, and Customer Support prepares for customer inquiries. All these departments must collaborate closely to ensure a successful launch, sharing information, coordinating timelines, and working toward the common goal.
Tips for Improving Interdepartmental Collaboration
Successful inter departmental collaboration doesn’t happen by chance—it requires intentional effort and the right strategies. In this section, we’ll explore practical tips and proven approaches that organizations can implement to enhance collaboration between departments, from establishing effective meeting practices to creating supportive technological infrastructure.
Regular meetings and discussions
Effective inter departmental meetings serve as the foundation for successful collaboration. To make these meetings productive:
- Schedule regular touchpoints at consistent times that work for all departments
- Create structured agendas that balance updates, discussion, and problem-solving
- Rotate meeting facilitation between departments to ensure diverse perspectives
- Document and share meeting outcomes and action items promptly
- Include both strategic discussions and tactical planning to keep all levels engaged
Open communication
Creating robust channels for communication helps break down departmental silos:
- Implement collaboration platforms that support both formal and informal communication
- Create dedicated channels for specific projects or initiatives
- Establish clear guidelines for communication frequency and response times
- Encourage the sharing of departmental updates and achievements
- Foster an environment where questions and concerns can be raised without fear
Joint planning
Effective collaboration requires coordinated planning efforts:
- Begin projects with inter departmental planning sessions
- Create shared project timelines that account for each department’s constraints
- Define clear roles and responsibilities across departments
- Establish shared metrics for success
- Regularly review and adjust plans based on collective feedback
Invest in training
Training is crucial for building collaborative capabilities:
- Provide communication skills workshops focusing on inter-departmental interaction
- Offer conflict resolution training to help teams navigate disagreements
- Conduct technical training on collaborative tools and platforms
- Develop cultural awareness training for better understanding between departments
- Include team-building exercises that bring different departments together
The role of management
Leadership plays a critical role in fostering collaboration:
- Leaders should model collaborative behavior in their own interactions
- Managers need to actively remove barriers to inter-departmental work
- Executive support should be visible and consistent
- Performance evaluations should include collaborative metrics
- Resources must be allocated to support collaborative initiatives
Create a common information environment
A unified technological infrastructure supports seamless collaboration:
- Implement shared project management platforms accessible to all departments
- Use centralized calendaring solutions like Virto Calendar App for SharePoint Online & Microsoft 365 to coordinate activities
- Utilize collaborative tools within Microsoft Teams to create a single source of truth
- Ensure all departments have equal access to necessary data and resources
- Standardize file sharing and documentation practices across departments
Recognize success
Celebrating collaborative achievements reinforces positive behaviors:
- Acknowledge successful inter-departmental projects in company communications
- Create awards or recognition programs for exceptional collaboration
- Share success stories during company meetings
- Highlight individual contributions to collaborative efforts
- Use successful collaborations as case studies for future initiatives
By implementing these tips, organizations can create a strong foundation for effective interdepartmental cooperation. Remember that improving collaboration is an ongoing process that requires regular assessment and adjustment to maintain its effectiveness. Success comes from consistent effort, clear communication, and a genuine commitment to working together across departmental boundaries.
What Are Examples of Interdepartmental?: Examples of Successful Interdepartmental Collaboration
Real-world examples help illustrate how effective interdepartmental coordination creates tangible benefits for organizations. In this section, we’ll explore four specific scenarios where different departments work together to achieve superior results, demonstrating the practical application of collaborative principles.
Marketing and Sales collaboration: Promoting new products
Let’s explore the collaborative synergy between Marketing and Sales, specifically regarding new product promotion. The success of a new product hinges on effective communication and a unified approach between these two crucial departments. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of how this collaboration can play out:
Shared understanding of the target audience:
- Sales contribution: The sales team, through direct interaction with customers, possesses invaluable insights into customer needs, pain points, preferences, and buying behaviors. They can provide specific examples of customer feedback, objections, and frequently asked questions. This information forms the foundation for a targeted marketing strategy.
- Marketing application: Marketing uses this data to create detailed buyer personas, representing the ideal customer for the new product. This helps tailor messaging and choose the right channels to reach the target audience effectively.
Jointly developed marketing campaigns:
- Sales input: Sales can provide feedback on the messaging, ensuring it resonates with the language and concerns of potential customers. They can also identify key selling points that should be emphasized in the marketing materials.
- Marketing execution: Marketing develops targeted campaigns across various channels, including email marketing, social media advertising, content marketing, and search engine optimization (SEO), all informed by the sales team’s input.
Lead generation and qualification:
- Marketing’s role: Marketing campaigns are designed to generate leads – potential customers interested in the new product. They use various tactics to capture leads, such as landing pages, forms, and calls to action.
- Sales follow-up: Sales receives these qualified leads from marketing and follows up with personalized outreach, nurturing the leads through the sales funnel. The clear handoff process ensures no leads are lost and that sales has the context necessary for effective engagement.
Closed-loop feedback system:
- Sales feedback: Sales provides feedback to marketing on the quality of the leads generated, the effectiveness of the messaging, and any insights gleaned from customer interactions.
- Marketing optimization: Marketing uses this feedback to refine future campaigns, adjust targeting parameters, and optimize messaging for improved conversion rates. This creates a continuous improvement loop, ensuring that marketing and sales efforts are constantly aligned and optimized for maximum impact.
Example:
Consider a software company launching a new project management tool. Sales identifies that their target audience struggles with inefficient workflows and lack of team transparency. Marketing uses this information to create a campaign highlighting the tool’s features that address these specific pain points. They create blog posts, social media ads, and email sequences showcasing how the tool streamlines workflows and improves team communication. Sales then uses these targeted materials to engage with leads, demonstrating how the software directly addresses their needs. This collaborative approach ensures a consistent message and maximizes the chances of converting leads into paying customers.
By working together, marketing and sales can create a powerful synergy that drives new product adoption and contributes significantly to the overall success of the organization.
HR and IT partnership: Modernizing workforce management
Let’s explore the collaboration between HR and IT in automating HR processes. This partnership is crucial for modern organizations seeking to improve efficiency, accuracy, and employee experience.
Needs identification and assessment:
- HR’s role: HR takes the lead in identifying areas where automation can bring significant improvements. They analyze existing processes, pinpoint bottlenecks, and gather requirements for new systems. This might involve surveying employees, analyzing workflow inefficiencies, or identifying compliance requirements. Examples include automating time and attendance tracking, streamlining onboarding processes, managing employee performance reviews, or centralizing learning and development resources.
- IT’s input: IT collaborates with HR to assess the feasibility of different automation solutions, considering factors like existing IT infrastructure, budget constraints, security requirements, and integration with other systems.
System selection and implementation:
- Joint decision-making: HR and IT work together to select the most suitable HRMS or other automation tools. HR focuses on features that meet their specific needs, while IT ensures the chosen system aligns with the organization’s technical capabilities and security standards. This joint decision-making process ensures that the chosen solution meets the needs of both departments and the organization as a whole.
- IT’s technical expertise: IT takes the lead in implementing and configuring the chosen system, ensuring seamless integration with existing IT infrastructure. They handle data migration, system setup, user training, and ongoing technical support.
Training and change management:
- HR’s focus on user adoption: HR plays a key role in training employees on how to use the new system effectively. They develop training materials, conduct workshops, and provide ongoing support to ensure smooth user adoption.
- IT’s technical assistance: IT provides technical assistance during the training process and addresses any technical issues that arise. They also ensure that the system is user-friendly and accessible to all employees.
Ongoing maintenance and support:
- IT’s system management: IT is responsible for maintaining the system, ensuring its security, and providing ongoing technical support to users. They also manage system updates and upgrades.
- HR’s feedback and optimization: HR provides feedback to IT on the system’s performance, identifies areas for improvement, and suggests enhancements to better meet evolving HR needs.
Example:
Imagine a company struggling with manual leave request processing. Employees submit paper forms, which are then routed through multiple departments for approval. This process is time-consuming, prone to errors, and lacks transparency. HR collaborates with IT to implement an automated leave management system. IT sets up the system, integrates it with the company’s payroll system, and provides training to employees. As a result, leave requests are processed much faster, errors are minimized, and employees have real-time visibility into their leave balances and request status.
By fostering a strong collaborative relationship, HR and IT can effectively leverage technology to automate HR processes, resulting in significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, employee satisfaction, and overall organizational performance.
Improve Your Collaboration with Virto Apps
Product and support team integration: Customer-driven innovation
Now, let’s explore how combined efforts of the Product Department and the Support Team lead to product improvement and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Gathering and categorizing customer feedback:
- Support team’s role: The Support Team acts as the primary point of contact for customers, handling inquiries, troubleshooting issues, and gathering valuable feedback. They meticulously document customer interactions, noting recurring problems, feature requests, and general feedback on the product’s usability and performance. Crucially, they categorize these issues by type, severity, and frequency.
- Tools and processes: Using helpdesk software, CRM systems, or other feedback collection tools, the Support Team can efficiently track and categorize customer issues, making it easier to identify trends and prioritize areas for improvement.
Communicating insights to the product team:
- Regular communication channels: Establishing regular communication channels between the Support Team and the Product Team is essential. This could involve weekly meetings, shared dashboards, or dedicated communication platforms where support can relay customer feedback and insights.
- Prioritization and impact assessment: The Support Team doesn’t just relay raw data; they analyze the feedback and provide context to the Product Team. They highlight the impact of each issue on customer satisfaction, the frequency of occurrence, and the potential consequences of not addressing the problem.
Product team analysis and prioritization:
- Understanding user needs: The Product Team analyzes the feedback received from the Support Team to gain a deeper understanding of user needs, pain points, and desired improvements. They consider the feasibility of implementing suggested changes, balancing customer needs with technical constraints and business priorities.
- Prioritizing development efforts: Based on the analysis, the Product Team prioritizes bug fixes, feature enhancements, and new feature development. They use a data-driven approach to determine which issues to address first, focusing on those with the biggest impact on customer satisfaction and business objectives.
Implementation and feedback loop:
- Development and testing: The Product Team develops and tests solutions to address the identified issues. They may involve the Support Team in the testing process to ensure the solutions effectively address the problems from the customer’s perspective.
- Communication and release: Once implemented, the Product Team communicates the changes to the Support Team, providing them with the information they need to assist customers with the updated product. The Support Team then monitors customer feedback on the implemented changes, providing further feedback to the Product Team, creating a continuous improvement loop.
Example:
Imagine a SaaS company offering an online collaboration platform. The Support Team notices a recurring issue where users struggle to share files larger than a certain size. They communicate this issue to the Product Team, highlighting the frustration it causes users and the potential impact on customer churn. The Product Team investigates the issue, prioritizes a solution, and develops a feature that allows for larger file uploads. They communicate the update to the Support Team, who then informs customers about the improvement. This collaborative process not only solves a specific problem but also strengthens the product and enhances customer satisfaction.
By fostering a strong partnership between the Product Department and the Support Team, companies can create a user-centric product development process that continuously evolves to meet customer needs, resulting in a stronger product offering and increased customer loyalty.
Production and logistics synchronization: Optimizing supply chain efficiency
Let’s delve deeper into the critical collaboration between Production and Logistics, highlighting how their coordinated efforts optimize supply chain efficiency and reduce costs.
Shared production planning and forecasting:
- Production’s role: The Production department develops detailed production schedules, outlining planned production volumes, timelines, and resource allocation. They also provide forecasts for future production output, considering factors like raw material availability, equipment capacity, and potential disruptions.
- Logistics’ input: Logistics contributes to production planning by providing insights into transportation lead times, warehouse capacity, and potential logistical bottlenecks. This collaborative planning process ensures that production schedules are realistic and aligned with logistical capabilities.
Real-time information sharing:
- Production updates: Production provides real-time updates to Logistics regarding production progress, any delays or disruptions, and the availability of finished goods. This transparency allows Logistics to adjust their plans dynamically.
- Logistics visibility: Logistics shares information with Production regarding warehouse capacity, transportation availability, and delivery schedules. This visibility allows Production to adjust production schedules if necessary to avoid bottlenecks and optimize inventory levels. This bidirectional information flow is crucial for maintaining a synchronized and efficient supply chain.
Optimized transportation and warehousing:
- Logistics planning: Based on real-time production data, Logistics optimizes transportation routes, consolidates shipments, and coordinates delivery schedules to minimize transportation costs and ensure timely delivery. They leverage route optimization software and transportation management systems to enhance efficiency.
- Warehouse management: Collaboration allows for efficient warehouse management. Logistics can anticipate incoming shipments and plan accordingly, minimizing storage time and reducing warehousing costs. They can also implement just-in-time inventory strategies, reducing the need for large buffer stocks.
Inventory management and control:
- Minimizing inventory holding costs: By coordinating production with logistics, companies can minimize inventory holding costs. Production avoids overproducing goods that would sit idle in warehouses, while Logistics ensures that finished goods are shipped promptly, reducing storage time and associated costs.
- Preventing stockouts: Effective collaboration helps prevent stockouts by ensuring that finished goods are available when and where they are needed. Real-time communication allows Logistics to anticipate potential shortages and adjust transportation plans accordingly.
Example:
A manufacturing company produces custom-ordered furniture. Production provides Logistics with a detailed production schedule for the upcoming week, including the estimated completion dates for each order. Logistics uses this information to schedule transportation, ensuring that trucks are available to pick up finished goods as soon as they are ready. This coordinated approach minimizes storage time in the factory warehouse, reduces transportation costs by optimizing routes, and ensures timely delivery to customers. If a production delay occurs, Production immediately informs Logistics, who can then adjust transportation schedules to avoid unnecessary truck idling time and maintain delivery commitments.
By fostering a strong collaborative relationship between Production and Logistics, companies can create a highly efficient and responsive supply chain, minimizing delays, reducing costs, and improving overall organizational performance.
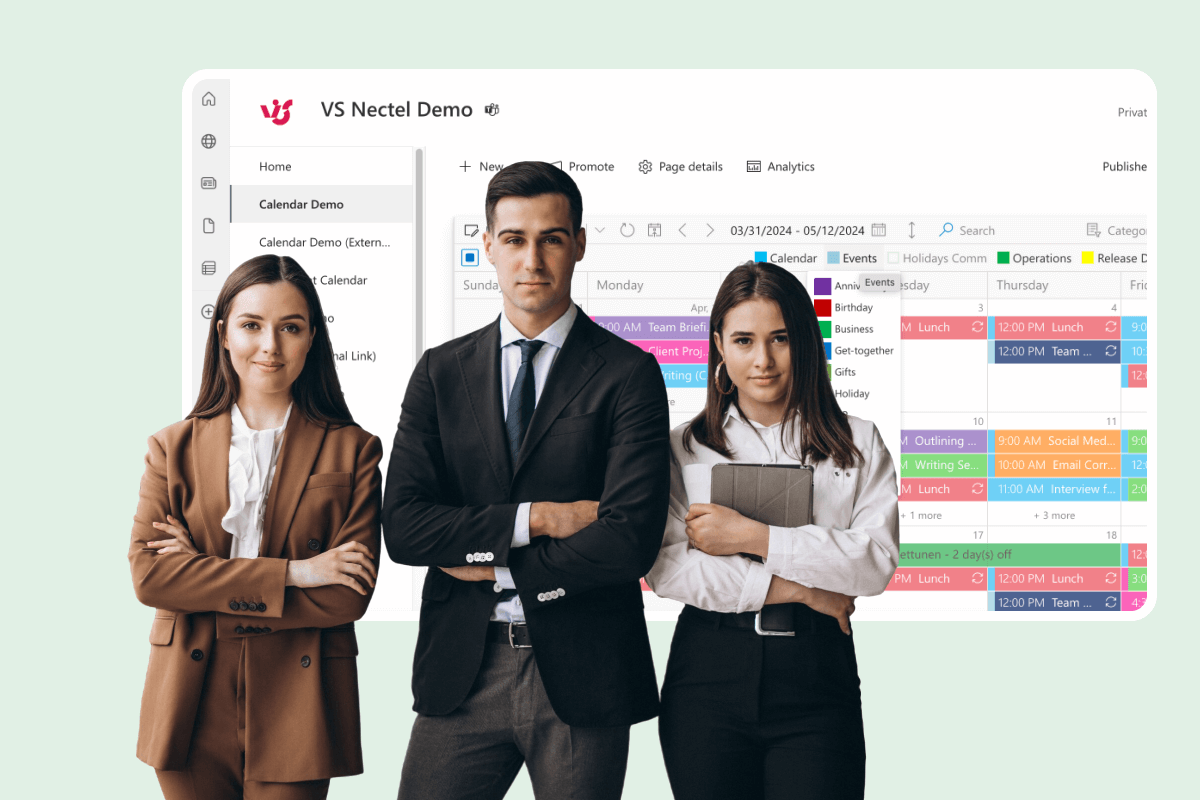
Using Virto Calendar App to Improve Interdepartmental Collaboration
This section explores how the Virto Calendar App can be a valuable tool for enhancing interdepartmental cooperation within organizations, particularly large organizations with complex scheduling needs. By centralizing scheduling, streamlining communication, and providing a unified view of events and tasks, Virto Calendar helps break down silos and foster a more collaborative work environment.
Key features and benefits for interdepartmental coordination:
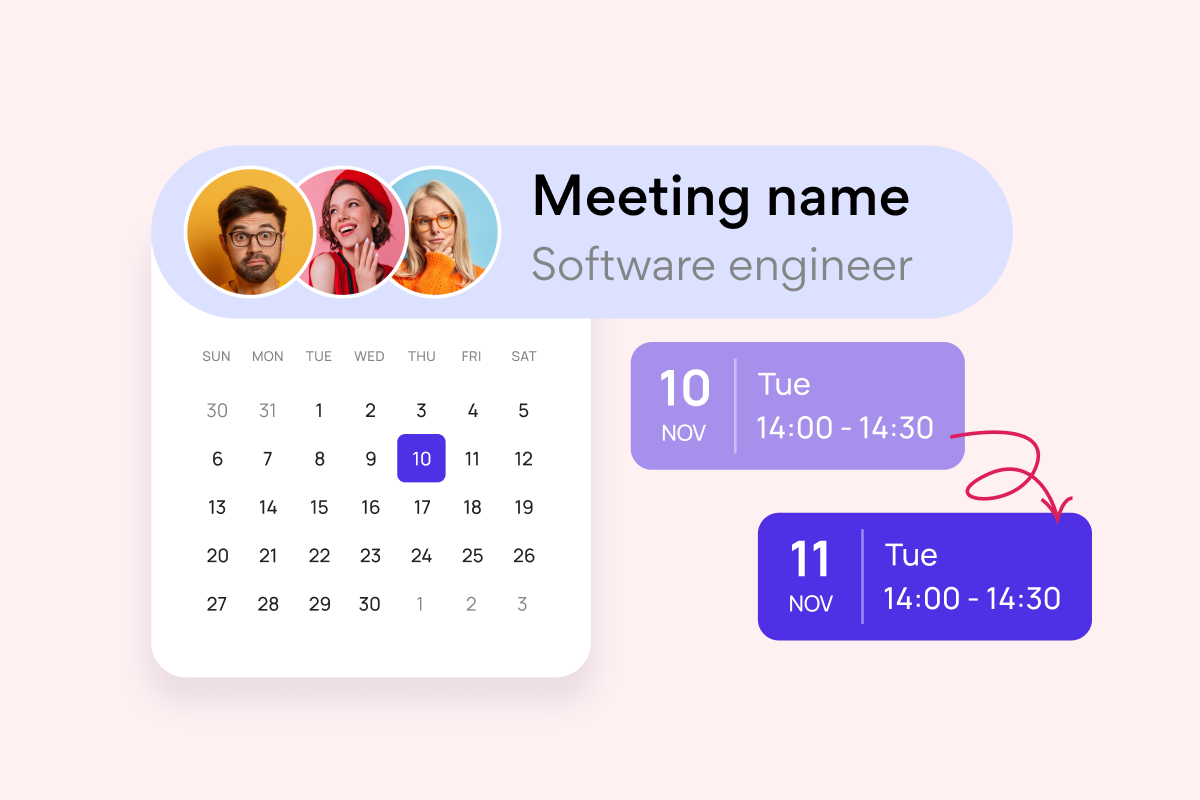
- Scheduling meetings and coordinating tasks: Virto Calendar simplifies the process of scheduling meetings across departments by providing a centralized platform where everyone can view availability and book meeting rooms or resources. The ability to overlay multiple calendars allows teams to easily identify suitable meeting times that accommodate everyone’s schedules. Furthermore, tasks can be integrated into the calendar, providing a comprehensive view of project timelines and deadlines.
- Simplifying communication between departments: By providing a shared view of events and deadlines, Virto Calendar enhances communication and transparency between departments. Everyone has access to the same information, minimizing the risk of miscommunication and scheduling conflicts. This shared understanding of timelines and deliverables facilitates smoother collaboration and improves project coordination.
- Eliminating schedule conflicts: The calendar overlay feature, a core functionality of Virto Calendar (refer to Virto’s documentation for details on calendar overlays), allows users to visualize the schedules of multiple departments simultaneously. This clear overview helps identify and resolve potential scheduling conflicts proactively, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently and projects stay on track.
Creating a common calendar for collaborative processes:
Virto Calendar enables the creation of a shared calendar specifically for employees involved in a collaborative process, regardless of their department. This shared calendar can include events, deadlines, milestones, and tasks related to the specific project or initiative. The calendar overlay feature allows participants to see their individual schedules alongside the shared project calendar, ensuring everyone stays aligned and informed.
Suitability for large organizations:
Virto Calendar is particularly well-suited for large organizations with numerous departments and complex scheduling needs. Its ability to integrate with various data sources, including SharePoint lists, Outlook calendars, Microsoft Planner, and external calendars via iCal feeds, allows for a comprehensive and unified view of organizational activities. This centralized approach simplifies coordination, reduces scheduling conflicts, and improves overall communication and collaboration across the organization.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we’ve explored how breaking down silos and fostering cooperation between departments can drive innovation, improve efficiency, and create a more dynamic and responsive organization.
The key to successful collaboration lies in understanding and addressing common challenges while implementing proven strategies for improvement. From establishing regular meetings to creating transparent communication channels, each step builds toward a more cohesive and effective organization. The benefits are clear: optimized processes, enhanced problem-solving capabilities, increased employee engagement, and ultimately, stronger business performance.
However, understanding the importance of collaboration is only the first step. Organizations must actively work to implement these practices and provide the necessary tools and support for their teams. This includes investing in appropriate technology solutions that facilitate seamless cooperation and communication between departments.
The Virto Calendar App for SharePoint Online & Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Teams stands out as a powerful tool for achieving these goals. By providing a centralized platform for schedule management, task coordination, and inter-departmental communication, it helps organizations overcome many common collaboration challenges while streamlining their operations.
- Schedule a quick demo for the Virto Calendar App
- Install a free trial version of the app for SharePoint or Microsoft Teams
For organizations looking to deepen their understanding of effective collaboration and calendar management, we invite you to explore additional resources on our blog:
- Guide to Cross-Team Collaboration
- Comprehensive Microsoft Teams Calendar Guide
- Tutorial on Calendar Sharing
Remember, successful interdepartmental collaboration isn’t just about having the right tools or following a set of guidelines—it’s about creating a culture where cooperation and shared success are valued and celebrated.